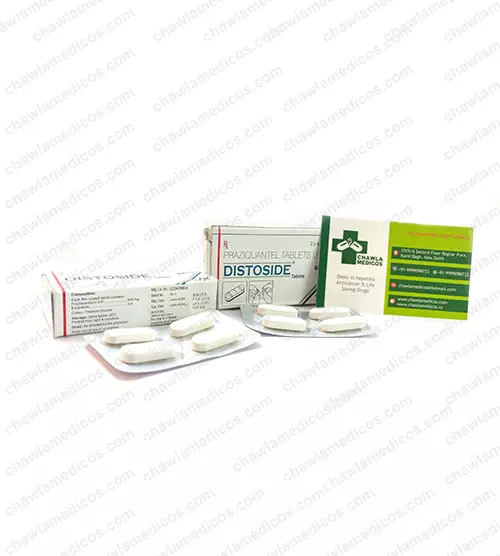
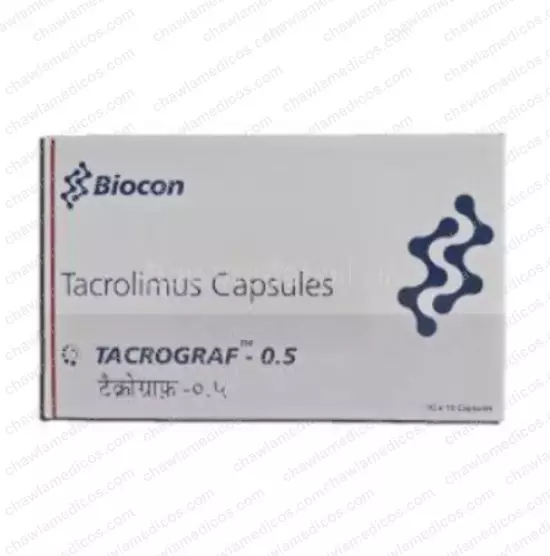
MEDICAL DISCLAIMER
Chawla Medicos only express opinions and provide information. All Trademarks, Brands and Service marks that appear on this website belong to their respective owner. We do not recommend any drug or give medical advice. Whether a medication is right for you is a decision between you and the prescribing doctor. The content of this site should not be a substitute for professional medical advise, diagnosis or any treatment. Above information is meant for: Wholesalers, Suppliers, Doctors, Hospitals, Clinics, Resellers,Medical Institutions and Pharmacies.